New AI Study Tackles the Transparency Problem in Black-Box Models
:::info Authors:
(1) Avi Schwarzschild, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland, USA and Work completed while working at Arthur (avi1umd.edu);
(2) Max Cembalest, Arthur, New York City, New York, USA;
(3) Karthik Rao, Arthur, New York City, New York, USA;
(4) Keegan Hines, Arthur, New York City, New York, USA;
(5) John Dickerson†, Arthur, New York City, New York, USA ([email protected]).
:::
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
1.1 Post Hoc Explanation
1.2 The Disagreement Problem
1.3 Encouraging Explanation Consensus
-
Related Work
-
Pear: Post HOC Explainer Agreement Regularizer
-
The Efficacy of Consensus Training
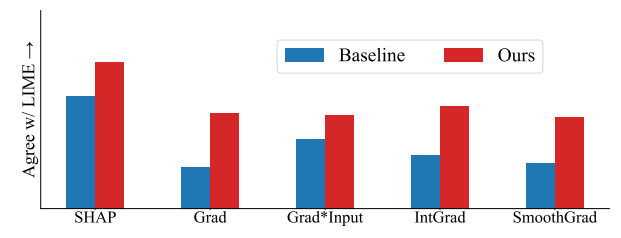
4.1 Agreement Metrics
4.2 Improving Consensus Metrics
[4.3 Consistency At What Cost?]()
4.4 Are the Explanations Still Valuable?
4.5 Consensus and Linearity
4.6 Two Loss Terms
-
Discussion
5.1 Future Work
5.2 Conclusion, Acknowledgements, and References
Appendix
ABSTRACT
As neural networks increasingly make critical decisions in highstakes settings, monitoring and explaining their behavior in an understandable and trustworthy manner is a necessity. One commonly used type of explainer is post hoc feature attribution, a family of methods for giving each feature in an input a score corresponding to its influence on a model’s output. A major limitation of this family of explainers in practice is that they can disagree on which features are more important than others. Our contribution in this paper is a method of training models with this disagreement problem in mind. We do this by introducing a Post hoc Explainer Agreement Regularization (PEAR) loss term alongside the standard term corresponding to accuracy, an additional term that measures the difference in feature attribution between a pair of explainers. We observe on three datasets that we can train a model with this loss term to improve explanation consensus on unseen data, and see improved consensus between explainers other than those used in the loss term. We examine the trade-off between improved consensus and model performance. And finally, we study the influence our method has on feature attribution explanations.
1 INTRODUCTION
As machine learning becomes inseparable from important societal sectors like healthcare and finance, increased transparency of how complex models arrive at their decisions is becoming critical. In this work, we examine a common task in support of model transparency that arises with the deployment of complex black-box models in production settings: explaining which features in the input are most influential in the model’s output. This practice allows data scientists and machine learning practitioners to rank features by importance – the features with high impact on model output are considered more important, and those with little impact on model output are considered less important. These measurements inform how model users debug and quality check their models, as well as how they explain model behavior to stakeholders.
1.1 Post Hoc Explanation
The methods of model explanation considered in this paper are post hoc local feature attribution scores. The field of explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) is rapidly producing different methods of this
\ 
\ type to make sense of model behavior [e.g., 21, 24, 30, 32, 37]. Each of these methods has a slightly different formula and interpretation of its raw output, but in general they all perform the same task of attributing a model’s behavior to its input features. When tasked to explain a model’s output with a corresponding input (and possible access to the model weights), these methods answer the question, “How influential is each individual feature of the input in the model’s computation of the output?”
\ Data scientists are using post hoc explainers at increasing rates – popular methods like LIME and SHAP have had over 350 thousand and 6 million downloads of their Python packages in the last 30 days, respectively [23].
1.2 The Disagreement Problem
The explosion of different explanation methods leads Krishna et al. [15] to observe that when neural networks are trained naturally, i.e. for accuracy alone, often post hoc explainers disagree on how much different features influenced a model’s outputs. They coin the term the disagreement problem and argue that when explainers disagree about which features of the input are important, practitioners have little concrete evidence as to which of the explanations, if any, to trust.
\ There is an important discussion around local explainers and their true value in reaching the communal goal of model transparency and interpretability [see, e.g., 7, 18, 29]; indeed, there are ongoing discussions about the efficacy of present-day explanation methods in specific domains [for healthcare see, e.g., 8]. Feature importance estimates may fail at making a model more transparent when the model being explained is too complex to allow for easily attributing the output to the contribution of each individual feature.
\ In this paper, we make no normative judgments with respect to this debate, but rather view “explanations” as signals to be used alongside other debugging, validation, and verification approaches in the machine learning operations (MLOps) pipeline. Specifically, we take the following practical approach: make the amount of explanation disagreement a controllable model parameter instead of a point of frustration that catches stakeholders off-guard.
1.3 Encouraging Explanation Consensus
Consensus between two explainers does not require that the explainers output the same exact scores for each feature. Rather, consensus between explainers means that whatever disagreement they exhibit can be reconciled. Data scientists and machine learning practitioners say in a survey that explanations are in basic agreement if they satisfy agreement metrics that align with human intuition, which provides a quantitative way to evaluate the extent to which consensus is being achieved [15]. When faced with disagreement between explainers, a choice has to be made about what to do next – if such an arbitrary crossroads moment is avoidable via specialized model training, we believe it would be a valuable addition to a data scientist’s toolkit.
\ We propose, as our main contribution, a training routine to help alleviate the challenge posed by post hoc explanation disagreement. Achieving better consensus between explanations does not provide more interpretability to a model inherently. But, it may lend more trust to the explanations if different approaches to attribution agree more often on which features are important. This gives consensus the practical benefit of acting as a sanity check – if consensus is observed, the choice of which explainer a practitioner uses is less consequential with respect to downstream stakeholder impact, making their interpretation less subjective.
2 RELATED WORK
Our work focuses on post hoc explanation tools. Some post hoc explainers, like LIME [24] and SHAP [21], are proxy models trained atop a base machine learning model with the sole intention of “explaining” that base model. These explainers rely only on the model’s inputs and outputs to identify salient features. Other explainers, such as Vanilla Gradients (Grad) [32], Gradient Times Input (Grad*Input) [30], Integrated Gradients (IntGrad) [37] and SmoothGrad [34], do not use a proxy model but instead compute the gradients of a model with respect to input features to identify important features.[1] Each of these explainers has its quirks and there are reasons to use, or not use, them all—based on input type, model type, downstream task, and so on. But there is an underlying pattern unifying all these explanation tools. Han et al. [12] provide a framework that characterizes all the post hoc explainers used in this paper as different types of local-function approximation. For more details about the individual post hoc explainers used in this paper, we refer the reader to the individual papers and to other works about when and why to use each one [see, e.g., 5, 13].
\ We build directly on prior work that defines and explores the disagreement problem [15]. Disagreement here refers to the difference in feature importance scores between two feature attribution methods, but can be quantified several different ways as are described by the metrics Krishna et al. [15] define and use. We describe these metrics in Section 4.
\ The method we propose in this paper relates to previous work that trains models with constraints on explanations via penalties on the disagreement between feature attribution scores and handcrafted ground-truth scores [26, 27, 41]. Additionally, work has been done to leverage the disagreement between different posthoc explanations to construct new feature attribution scores that improve metrics like stability and pairwise rank agreement [2, 16, 25].
\
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\
You May Also Like

Crucial Fed Rate Cut: Powell’s Bold Risk Management Move Explained

Why Vitalik Buterin Just Pulled 16,384 ETH From His Holdings

