Visual Prompt Generation: Cross-Attention in Q-Former
Table of Links
Abstract and 1 Introduction
-
Related Work
2.1. Multimodal Learning
2.2. Multiple Instance Learning
-
Methodology
3.1. Preliminaries and Notations
3.2. Relations between Attention-based VPG and MIL
3.3. MIVPG for Multiple Visual Inputs
3.4. Unveiling Instance Correlation in MIVPG for Enhanced Multi-instance Scenarios
-
Experiments and 4.1. General Setup
4.2. Scenario 1: Samples with Single Image
4.3. Scenario 2: Samples with Multiple Images, with Each Image as a General Embedding
4.4. Scenario 3: Samples with Multiple Images, with Each Image Having Multiple Patches to be Considered and 4.5. Case Study
-
Conclusion and References
\ Supplementary Material
A. Detailed Architecture of QFormer
B. Proof of Proposition
C. More Experiments
\ 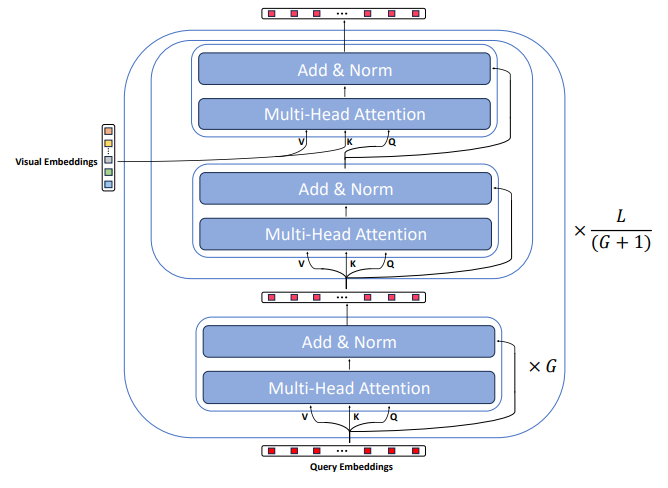
A. Detailed Architecture of QFormer
The architecture overview is depicted in Figure 7. Specifically, QFormer is initialized as a BERT-based model[8] comprising a total of L = 12 layers. In contrast to typical BERT models that process textual inputs, QFormer takes R = 32 learnable query embeddings as inputs. These embeddings are utilized to extract visual information from the input visual data during Stage-1 pretraining in BLIP2[22]. Subsequently, they serve as visual prompt embeddings for the LLM inputs after projection.
\ Inside the QFormer, each layer includes a self-attention module composed of a Multi-Head Attention component and a Forward module (consisting of Linear, LayerNorm, and Residual Connection). The cross-attention module, initialized with random values, is inserted every G layers, where learnable query embeddings interact with visual embeddings. In the main paper, for the sake of conciseness, we condensed the representation of the multi-head attention and forward modules into self(cross) attention modules. Furthermore, we exclusively illustrated the modifications made to the cross-attention module in MIVPG, as the self-attention modules remain unchanged. The final QFormer output is represented by the last layer’s query embeddings.
\ For a more comprehensive understanding, readers are encouraged to refer to [22].
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Wenliang Zhong, The University of Texas at Arlington ([email protected]);
(2) Wenyi Wu, Amazon ([email protected]);
(3) Qi Li, Amazon ([email protected]);
(4) Rob Barton, Amazon ([email protected]);
(5) Boxin Du, Amazon ([email protected]);
(6) Shioulin Sam, Amazon ([email protected]);
(7) Karim Bouyarmane, Amazon ([email protected]);
(8) Ismail Tutar, Amazon ([email protected]);
(9) Junzhou Huang, The University of Texas at Arlington ([email protected]).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC by 4.0 Deed (Attribution 4.0 International) license.
:::
\
You May Also Like
qLabs Fires First Shot in Quantum Crypto Race — Can Coinbase Catch Up?

The Anatomy of a Self-Made Billionaire’s Mindset: How Gurhan Kiziloz Reached a $1.7B Net Worth

