What If Your Electricity Came from Space?
Space-based solar power (SBSP) can change how we think about generating energy. Instead of being limited by Earth's weather and day-night cycle, SBSP systems work in the constant sunlight of space.
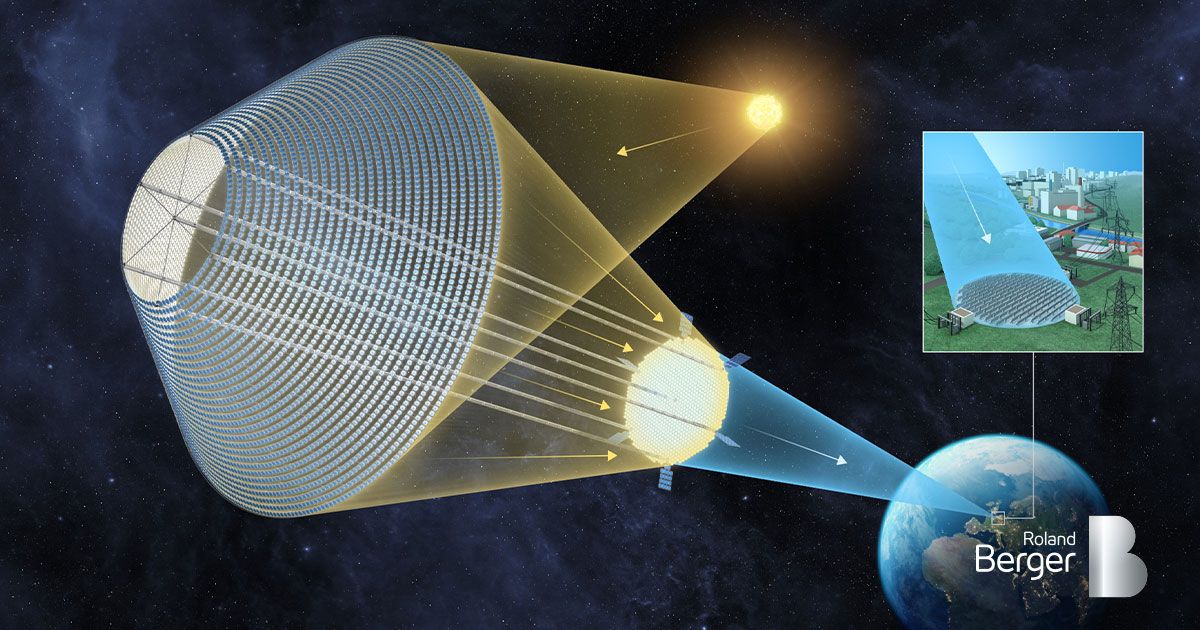
\ The idea is simple: put large solar panels in orbit, turn the energy into microwaves, and send it wirelessly to stations on Earth. This method is exciting because solar energy in space is always available and about eight times stronger than on Earth, all day, every day.
\ Countries like Japan, China, and the United States are investing in SBSP research to see if it can work and grow. Japan's OHISAMA program plans to show space-to-Earth power transmission in 2025, while China aims for kilometer-wide solar panels in space by the 2030s.
How SBSP Works
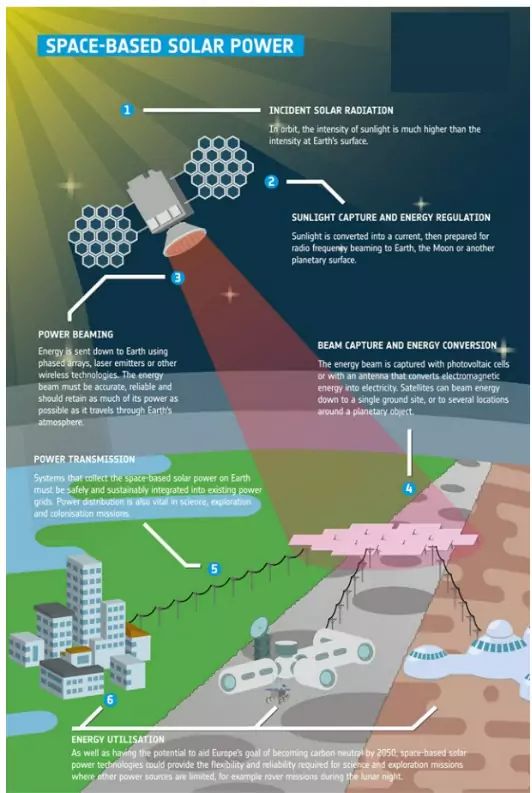
The basic setup of space-based solar power includes three main parts that work together to send energy from space to Earth.
Orbital Solar Arrays
Most SBSP designs imagine large solar panels placed in geostationary Earth orbit (GEO), about 22,000 miles above the equator. Here, satellites stay in the same spot relative to Earth's surface, allowing them to send power continuously to specific places on the ground.
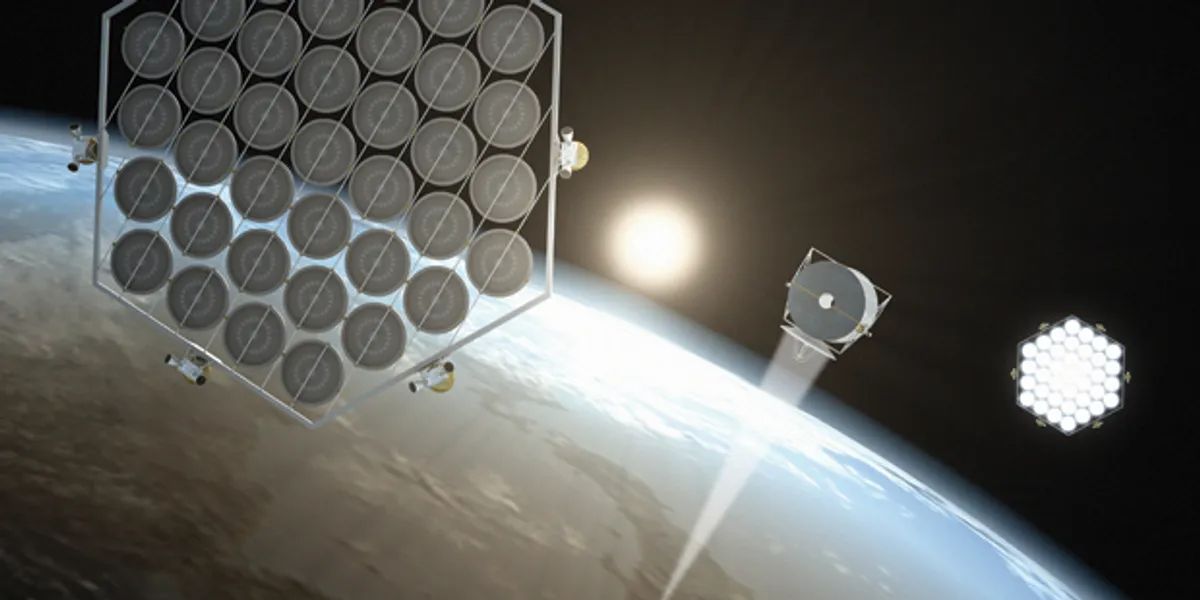

\ Other designs think about using low Earth orbit (LEO) groups at 400-1,200 miles high. These need more complex tracking and more satellites for continuous coverage but have lower launch costs and shorter distances for sending power. The solar panels use high-efficiency photovoltaic cells designed for space, achieving conversion efficiencies of 40-50% without atmospheric interference, much higher than solar panels on Earth.
Microwave Power Transmission
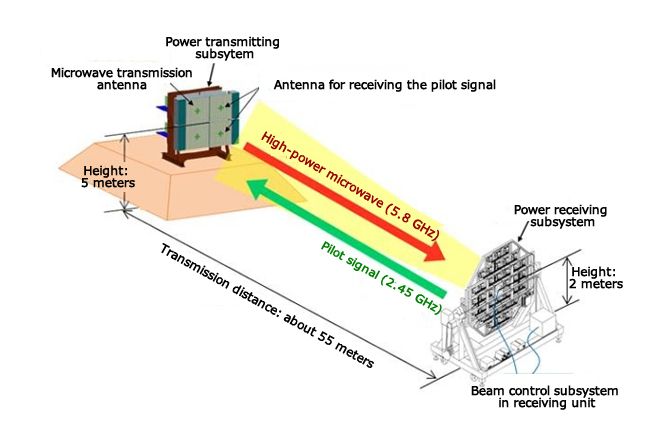
\ The solar energy collected is changed into microwaves to be sent wirelessly to Earth. This happens at frequencies between 2.45 GHz and 5.8 GHz to reduce atmospheric absorption and avoid disrupting current communication systems. The microwave beam is precisely aimed using phased array antennas, forming a narrow beam that sends power to specific receiving stations. The beam's strength is carefully managed to keep it safe for aircraft and wildlife that might cross its path.
Ground-Based Rectennas
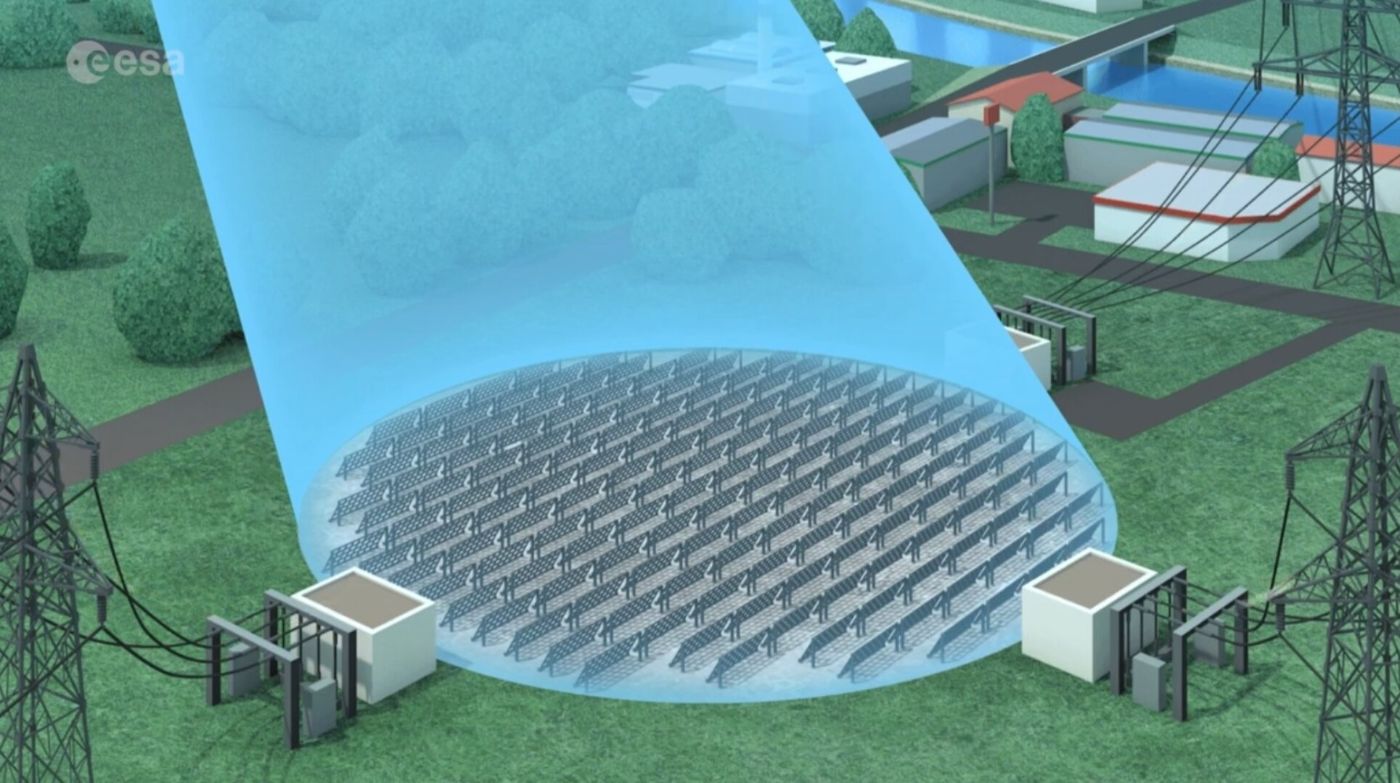

\ On Earth, special receiving antennas called rectennas capture the microwave energy and turn it back into electricity. These setups include arrays of dipole antennas with diodes that change the AC microwave signal into DC power.
Rectenna farms usually cover several square kilometers to effectively capture the transmitted beam. The converted electricity is then adjusted and fed into the existing power grid using standard power electronics
Earthside Benefits
Space-based solar power (SBSP) has many benefits that could change how we use renewable energy and manage power grids. Unlike solar and wind power on Earth, SBSP gives continuous and predictable energy, solving the problem of renewable energy being inconsistent.
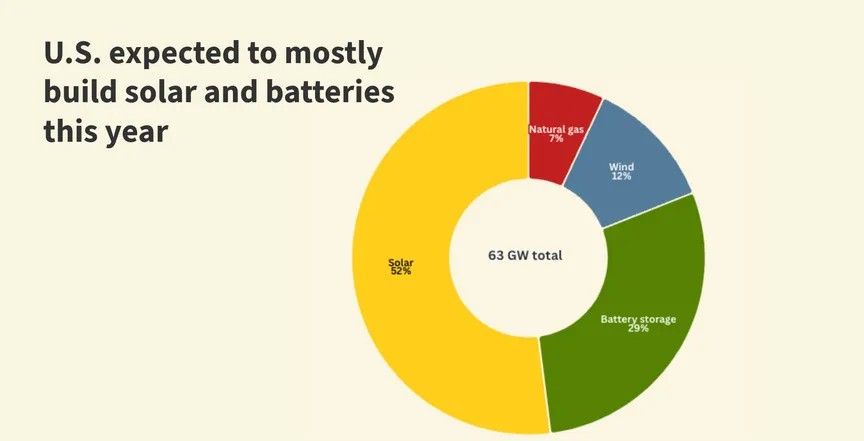
\ This steady power means we don't need big energy storage systems, which usually help balance out energy changes, making the shift to clean energy cheaper and simpler. SBSP can also send power to temporary stations, which is very helpful for disaster relief by quickly providing electricity to areas hit by hurricanes, earthquakes, or other disasters that damage ground infrastructure. Remote places like islands, mining sites, and military bases can get power without needing long transmission lines, which is useful where extending the grid isn't cost-effective. SBSP's reliability helps stabilize power grids by providing steady clean energy, reducing the need for fossil fuel backup plants. Large-scale SBSP could also lower electricity price changes by offering consistent low-cost energy, much like how nuclear power provides a steady energy supply.
Early Use Cases & Phased Deployment
The path to commercial space-based solar power will likely happen in stages, starting with specific uses before expanding to larger utility-level use. Japan's OHISAMA project is the first step, using a 180-kilogram satellite to send about 1 kilowatt of power from 400 kilometers up, enough for a household appliance but not yet at commercial scale. These early tests aim to prove key technologies: sending power from space to Earth, accurately directing beams, and efficient rectennas. Success here will show that bigger systems can work.
Initial commercial uses will focus on remote areas where power is costly or unavailable, like military bases, Arctic stations, and deep-sea platforms. Space-based power could also help lunar and Mars bases. For utility use, much larger installations are needed, which will require cheaper space access and construction. Utility partnerships and long-term deals will be important for funding, and government support could speed up deployment
Challenges
Space-based solar power has a lot of potential, but there are big technical, economic, and regulatory challenges to overcome before it can be widely used. Launching costs are high, making large-scale projects expensive. Even with SpaceX's Falcon Heavy lowering costs to about $1,400 per kilogram to GEO, launching large solar arrays would still cost tens of billions of dollars. Building these arrays in space is also tough, needing special robots, precise positioning, and the ability to work in harsh space conditions, so designs that can be put together automatically are important. Additionally, using microwaves to transmit power raises safety issues for planes, satellites, and living things, so power limits are needed to keep it safe while still being efficient.
International cooperation is needed to assign frequencies and orbital slots. The ITU and other regulatory bodies must set up rules for managing space-based power systems along with current satellite services. When microwaves pass through Earth's atmosphere, some energy can be lost, almost 100% efficiency in clear weather, but 2-5% less in heavy rain or clouds. Ground-based rectenna systems must manage changing power levels and might need backups during bad weather, which can reduce their reliability. SBSP systems need specific radio frequencies to avoid interfering with existing services, and there are only a few suitable frequencies, which might limit how much power can be sent at once. Working with satellite operators, radio astronomy, and wireless services is crucial, needing international agreements similar to those for satellite communications.
Path Forward
Creating commercially viable space-based solar power needs teamwork in different areas like technology, policy, and international collaboration. We need to improve high-efficiency solar cells for space, lightweight structures, and systems for building in orbit, as these will impact cost and feasibility. Rectenna technology also needs to be better to increase efficiency and reduce space on the ground, while solid-state power amplifiers and advanced beam-forming systems will make transmission more efficient and safe.
Governments should create rules for space-based power systems, including safety standards, to attract investment. Adding space-based solar power to carbon credits and renewable incentives can ensure stable income. International cooperation is needed to manage orbits and radio frequencies. Sharing technology and working together on missions can speed up development and reduce costs. Standard rectenna kits and modular parts can lower deployment costs, allowing for multiple suppliers. Recognizing the clean energy benefits in carbon credits can increase revenue. Connecting with existing renewable energy markets is essential for success
Conclusion
Space-based solar power could change clean energy by giving us constant power along with earth-based renewables. Although there are challenges, progress in space technology and interest from big agencies suggest that orbital power systems might work in the next twenty years. This will require investment, rules, and teamwork. If successful, space-based solar power could become important for global clean energy, working alongside land-based renewables. Together with solar, wind, hydro, and nuclear power, it could help reduce carbon emissions and meet global energy needs. The idea of endless clean energy from space might soon be possible, providing sustainable power for Earth and future space communities.
\
You May Also Like

Three Must-Attend Side Events at Korea Blockchain Week 2025

Kraken's Big Hint: Pi Coin Set for Exchange Listing In 2026
