Polkadot (DOT) in 2025: The Network of Networks Powering Interoperable Web3
 Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- Polkadot: A Network of Networks
- The Vision Behind Polkadot’s Creation
- How Polkadot’s Modular Technology Works
- Governance and Community Power
- Polkadot in Action: Examples and Partners
- DOT Tokenomics Explained
- Polkadot’s Roadmap and Future Outlook
- FAQ: 10 Unanswered Questions About Polkadot
 Polkadot: A Network of Networks
Polkadot: A Network of Networks
Polkadot is one of the most promising innovations in blockchain technology. Unlike traditional single-chain blockchains such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, Polkadot is designed as a network of blockchains. Through its modular architecture, it enables a wide range of specialized applications to run in parallel while benefiting from shared security and interoperability.
The native token DOT functions as a cryptocurrency, governance tool, and utility token. Its goal is to build an interoperable Web3 ecosystem where blockchains can communicate securely and efficiently. This design allows projects to develop custom solutions without compromising network stability or scalability.
 The Vision Behind Polkadot’s Creation
The Vision Behind Polkadot’s Creation
Polkadot was conceived by Dr. Gavin Wood, one of Ethereum’s co-founders, in 2016. His vision was to overcome the limitations of existing blockchains. The development is led by the Web3 Foundation and Parity Technologies. The mission: to build a decentralized internet free from gatekeepers, where users retain full control over their data and applications.
 How Polkadot’s Modular Technology Works
How Polkadot’s Modular Technology Works
Polkadot is built on a modular architecture with three key components:
- Relay Chain: The central chain providing security, governance, and transaction validation.
- Parachains: Independent blockchains that run in parallel, customized for specific applications like DeFi, gaming, or identity management.
- Bridges: Connect Polkadot with external blockchains such as Ethereum and Bitcoin, enhancing interoperability.
This design allows scalability, specialization, and seamless communication between blockchains.
 Governance and Community Power
Governance and Community Power
Unlike off-chain governance models, Polkadot implements on-chain governance. DOT holders directly vote on protocol upgrades, parameter adjustments, and feature integrations. This democratic model empowers the community and promotes transparency. A notable example is Parachain Auctions, where projects compete for relay chain slots, and the community votes on which projects are integrated.
 Polkadot in Action: Examples and Partner Projects
Polkadot in Action: Examples and Partner Projects
Polkadot supports a wide variety of applications, including:
- DeFi: Acala (stablecoins, financial products) and Parallel Finance (lending, staking, trading).
- Smart Contracts: Moonbeam, offering Ethereum compatibility for developers.
- Digital Identity: KILT Protocol, providing verifiable credentials.
- Other Sectors: Energy, logistics, and sustainability through collaborations with companies and NGOs.
| Project | Focus Area | Role within Polkadot |
|---|---|---|
| Acala | DeFi / Stablecoins | Financial hub for decentralized services |
| Moonbeam | Smart Contracts | Ethereum-compatible environment |
| KILT Protocol | Digital Identity | Identity verification and data management |
 DOT Tokenomics Explained
DOT Tokenomics Explained
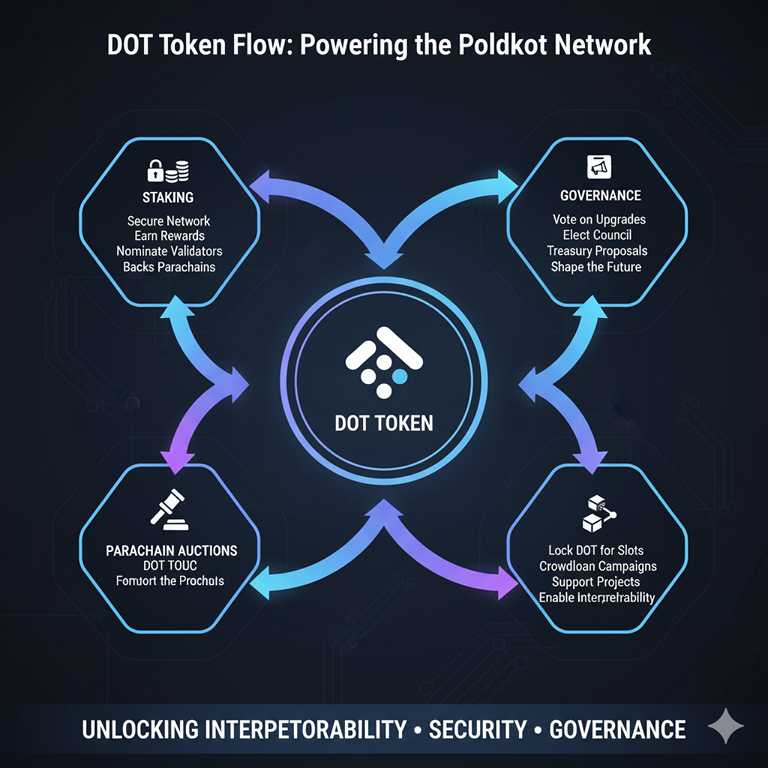
The DOT token underpins the economic model of Polkadot. Unlike capped-supply cryptocurrencies, DOT uses an inflation-based model to ensure continuous network incentives. Key functions include:
- Governance: Voting on protocol changes and new features.
- Staking: Securing the network by rewarding validators and nominators.
- Parachain Auctions: Funding slots on the relay chain for project integration.
 Polkadot’s Roadmap and Future Outlook
Polkadot’s Roadmap and Future Outlook
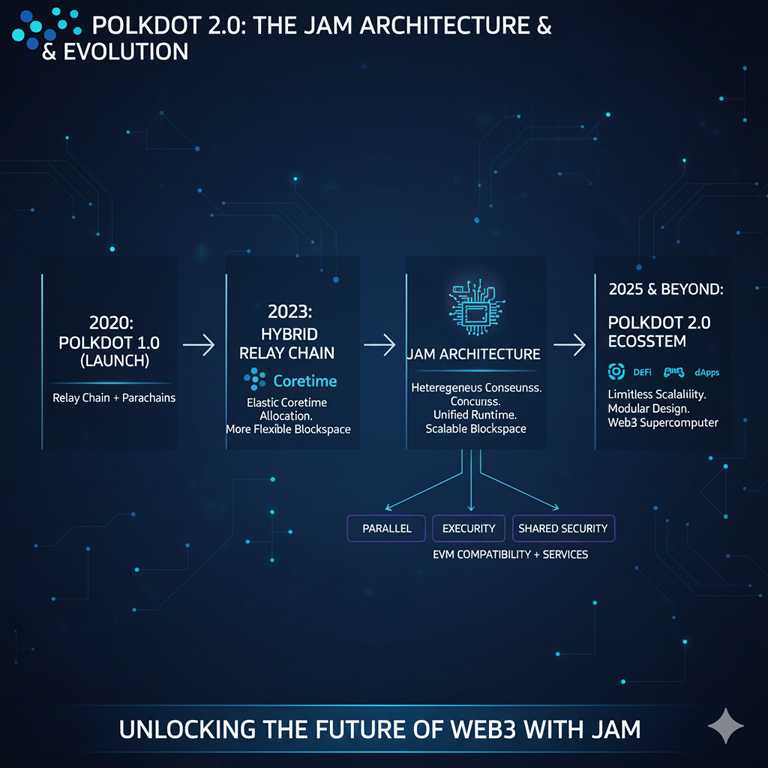
In 2025, Polkadot is focused on expanding its parachain ecosystem and building additional bridges to external networks. Regulatory clarity could accelerate institutional adoption. With its multi-chain architecture, Polkadot is becoming a key infrastructure provider for Web3.
The development of Polkadot 2.0 will transform the platform into a global computing environment. Its JAM architecture (Join-Accumulate Machine) introduces vertical scalability and service-oriented design, aiming to support decentralized Web3 cloud functions.
 FAQ: 10 Unanswered Questions About Polkadot
FAQ: 10 Unanswered Questions About Polkadot
]]>You May Also Like

Traders Call It the Top Crypto for 2025 With 45x Potential, While ADA and XRP Could Deliver But Small

MARA Produces 736 BTC While CleanSpark Mines 629 Bitcoin in September
